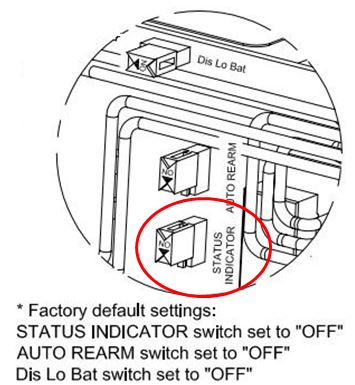
Status indicator is set to “Off” by default. The yellow slide switch for status indicator needs to be slid to on. The unit must be off and battery removed before the change can be made.
|
New price increase January 7, 2026
|
Status indicator is set to “Off” by default. The yellow slide switch for status indicator needs to be slid to on. The unit must be off and battery removed before the change can be made.

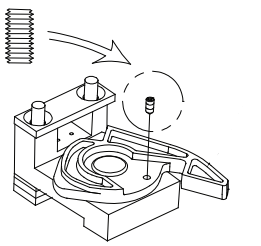
The Keystop feature is installed. This is a security feature that automatically turns the alarm on when the key is removed.
If you no longer want this feature, remove the filler plate from the bar and take out the keystop setscrew:
When it comes to electrified locks and exit devices, power transfers play a crucial role in ensuring seamless operation while maintaining security and aesthetics. Whether you’re planning new construction or retrofitting existing doors, selecting the right power transfer solution can make all the difference.
Power transfers provide a means of running wires from the door frame to electrified door hardware such as locks, strikes, or exit devices. They come in various forms, each suited to specific applications and installation requirements.
Power transfers are the unsung heroes of electrified door systems, ensuring reliable power delivery while maintaining security and aesthetics. By understanding the types and applications of power transfers, you can choose the right solution for your project, whether it’s a high-security facility, a retrofit, or a new construction.
For more information or assistance with selecting the ideal power transfer for your needs, feel free to reach out to our team.

Our world is full of threats both external and internal. This whitepaper encourages looking at life safety and security measures on your campus from another perspective. Most facilities have addressed access control and the securing of main doors, but those should be measures of last resort. There are steps you can take — some that you may not have considered — to mitigate the threat before it arrives at your front door.
But the threat isn’t always external. What about the daily safety of your students and staff? Measures to alert security personnel when unauthorized access or egress is about to occur can be put in place to prevent an incident before it happens.
Supplemental security measures, such as securing perimeter entrances and installing devices to warn when secondary entry points are compromised, can increase your ability to protect your campus against threats.
The questions facing the person responsible for campus safety and security are numerous. How do you allow authorized staff to move freely through your facility, accessing areas that are restricted to the general public, but still allow egress during an emergency? Are you vulnerable to an attack from a disgruntled staff member, begrudged student, or stranger off the street? How effective is your access control system if staff or students are propping doors open? Can we put controls in place, but still meet ADA requirements?
We give these threats little thought until the unthinkable is broadcast on national news and then we scramble to ensure our faculty and students are not exposed to such a threat.
Examining security and safety on your campus from a holistic viewpoint can help prevent these threats from materializing. Enhance life safety and security measures on your campus with the addition of cutting-edge technology that works in conjunction with your existing systems, such as:
Delayed egress devices in education facilities can protect lives. Check your local fire and safety codes before installing delayed egress equipment. By installing delayed egress exit devices, you can:

Playgrounds with emergency exit gates that open near a busy street can be cause for concern. Where life safety codes restrict traditional locking of these gates, weatherized delayed egress may be an acceptable application, depending on the authority having jurisdiction. Weatherized delayed egress systems:
Supplementing existing door security with door prop alarms helps maintain a more secure environment. A door left propped open, even for a few seconds, can provide an easy access point for threats. Door prop alarm hardware will:
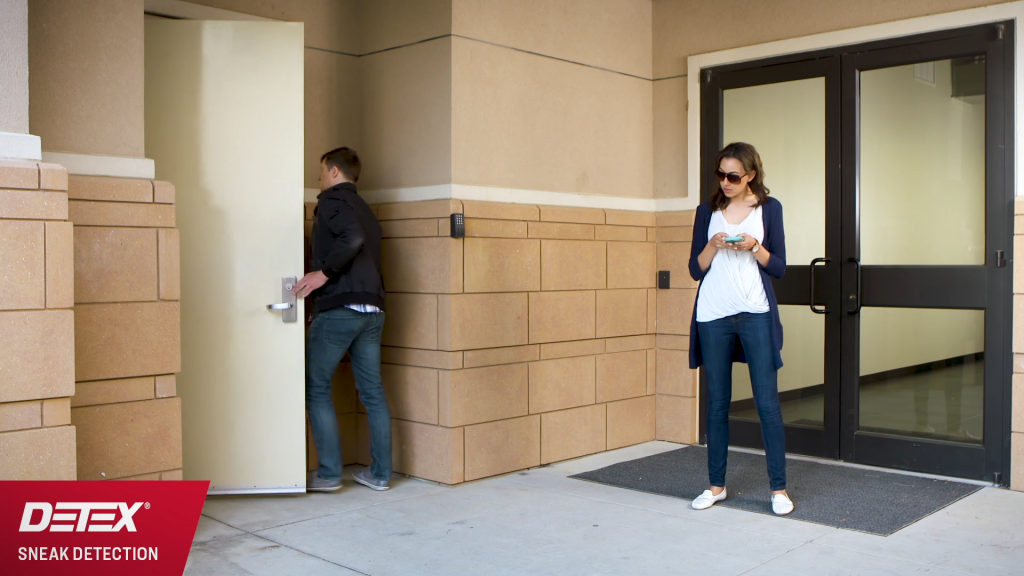

Access control systems and temporary visitor badges have become common in most school districts. However, regardless of the campus size, tailgate detection technology can be used to control access, allowing only authorized personnel access to to restricted areas. Tailgate detection systems will:
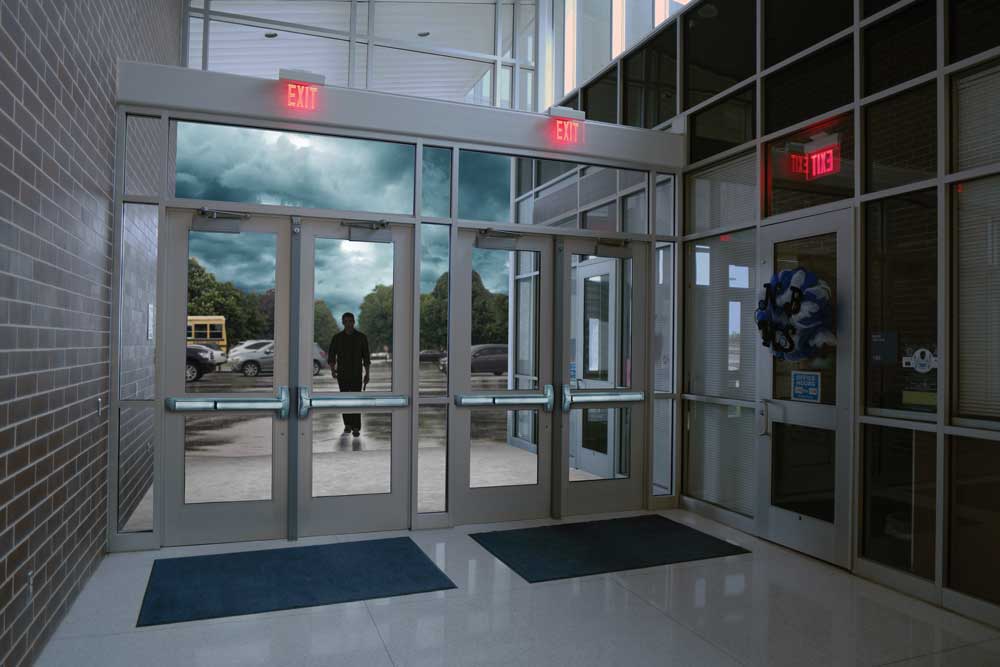

What is the safest, fastest, easiest and most cost effective means of locking down your campus? There are many answers; however, one way that has been overlooked by many security door consultants is the use of panic exit devices with electric dogging. When installed throughout a school facility, electric dogging allows all locking devices to be “energized” by one control switch that can be located in a centralized area of the building. Electric dogging:
(Be aware that add-on mechanical options like hex or cylinder dogging may jeopardize the effectiveness of the lockdown system.)
Electric dogging is different than electric latch retraction. With latch retraction, applying power pulls the latch(s) back and holds them until power is removed. With electric dogging, after applying power a user must manually depress the pushpad to retract the latch(s). The latches stay retracted until power is removed from the device.
When electric dogging is applied to entry doors, it removes the need for a staff member, perhaps in the height of a crisis, to remember where the key is and how to lockdown the doors. The administrator, taking the responsibility off the shoulders of the education staff, makes the decision and takes action to lockdown. Electric dogging can:
Ensuring all the pieces of technology will work together is key. Manufacturers and some dealers will create a kit to fit your application that includes best-in class products along with wiring and riser illustrations to fit your application. Be careful of specification writers who supply only a list of products without a wiring diagram or information on how the items are integrated together. Failing to install the items correctly can create years of headaches and wasted money. Ensure the supplier understands your needs and offers time-tested products. Additionally, make sure they can support the installation with wiring diagrams, riser illustrations and technical support.


| Rim | Mortise | |
| Cylinder Dogging (CD) | X | |
| Electric Unlock Trim (EU, EU2W, EUV) | X | |
| 08/09D, 08/09DN, 08/09DNV, 08/09DV | X | |
| 03WS, 03WSV | X | |
| 03C, 03CN, 03CNV, 03CV | X | |
| 03CM | X | |
| 03Z | X | |
| 03WM | X | |
| 03R | X | |
| 03CBK | X | |
| Hardwired Exit Alarm (EA) | X | |
| Weatherized Exit Alarm with Battery (EB W) | X | |
| Delayed Egress (EE) | X | |
| Electric Integration (EI) | X |

| Rim | Mortise | |
| Cylinder Dogging (CD) | X | |
| 03WS | X | |
| 03P, 03PN | X | |
| 03A, 03AN | X | |
| 08/09BN | X | |
| Electric Unlock Trim (EU2W) | X | |
| Hardwired Exit Alarm (EA) | X | |
| Exit Alarm with Battery (EB) | X | |
| Weatherized Exit Alarm with Battery (EB W) | X | |
| Delayed Egress (EE) | X |

| Rim | Mortise | |
| EAX-500 | X | |
| EAX-2500 | X | |
| EAX-3500 | X | |
| EAX-4200 | X | |
| EAX-300 | X |

| Rim | Mortise | |
| ECL-230D | X | |
| ECL-230X (TD, TDB, TB) | X | |
| ECL-600 | X | |
| ECL-620 | X |

| Rim | Mortise | |
| (F)90KR(E) | X |
| Rim | Mortise | |
| CS | X |
No facility is completely impervious to break-ins, but with the right security measures in place, you can make it much harder for burglars to succeed. The goal of break-in prevention is not to guarantee a completely secure building but to delay unauthorized entry long enough for law enforcement or security personnel to respond. Even if your building hasn’t experienced any recent security threats, regular evaluations and upgrades to its protective measures are essential.
Here’s a back-to-basics guide on how to fortify your facility’s entry points and deter potential break-ins.
The foundation of a secure entry point starts with the door itself. Even the strongest locks and security features will be ineffective if the door is weak.
In commercial settings, doors must swing outward to comply with egress codes, leaving the hinge knuckles exposed and vulnerable.
The lock is your first line of defense, so its strength should never be overlooked.
A robust alarm system can be a strong deterrent against intruders. Alarms alert authorities and make your facility a less attractive target. When paired with strong door hardware, alarms create a multi-layered security approach that is both proactive and responsive.
The most effective security comes from combining these elements:
Together, these components work to:
Break-in prevention is all about implementing strong, well-maintained hardware and a layered approach to security. Even small upgrades, like replacing standard hinges with full-length ones or adding a floor bolt, can greatly enhance the safety of your building.
If you’re ready to take the next step in securing your facility, contact our team for guidance on how to improve your security systems. Together, we can build a safer, more secure environment for your business.

Detex is proud to announce the addition of Yarimar Gonzalez to our team as the Engineering Test Lab Technician. In this vital role, Yarimar leads efforts to ensure product compliance with industry standards by conducting rigorous testing, maintaining the integrity of our quality assurance processes, and supporting agency certification requirements. She also reviews product drawings and installation instructions for accuracy, manages updates to the BHMA Certified Products Directory (CPD), and coordinates UL and Intertek recertification testing.
Yarimar is a U.S. Air Force veteran with 11 years of service as an Air-Launched Cruise Missile Maintenance Technician, including 7 years in supervisory roles. She brings extensive expertise in testing, troubleshooting, project management, integration, and life cycle logistics. Throughout her military career, Yarimar led critical phases of the missile life cycle—from maintenance and testing to shipping, receiving, and deployment—ensuring mission readiness and operational excellence.
She also has specialized experience in defense acquisitions, with a focus on testing and evaluating weapon systems. In her final military assignment, Yarimar served as Deputy Chief of Program Integration, where she led efforts to prepare a base for the fielding of a new weapon system.
In addition to her certification and compliance responsibilities, Yarimar supports regulatory audits, production testing, and technical troubleshooting, and maintains critical door fixtures and testing equipment. Her sharp attention to detail and leadership background make her a valuable asset in sustaining Detex’s reputation for safety, security, and reliability. She will also represent the company at customer sites and trade shows, collaborating across departments to support innovation and continuous improvement.
Yarimar brings a passion for growth and excellence to everything she does. With her technical knowledge and drive, she is well-positioned to make a strong impact as she helps advance Detex’s testing capabilities and product innovation.
Detex Corporation. All rights reserved.
